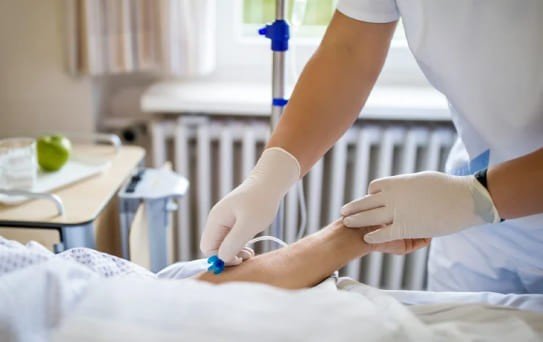
What Is Chelation?
Accumulation of metals such as lead, mercury, iron, and arsenic within the body can result in toxicity. Chelation therapy offers a treatment approach involving medication to eliminate these metals, preventing their harmful effects. The process of chelation therapy hinges on specialized drugs that bind to metal compounds present in the bloodstream. Administered via intravenous (IV) tube or oral pills, these chelating agents attach to the metals, facilitating their subsequent elimination from the body through urine.
How Chelation Treatment Works?
Metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic are susceptible to removal through chelation therapy. Before undergoing this treatment, a blood test is typically conducted to diagnose metal poisoning. During chelation therapy, a specific class of medication known as chelators or chelating agents is introduced through injection. Common examples include ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), dimercaptosuccinic acid, and dimercaprol.
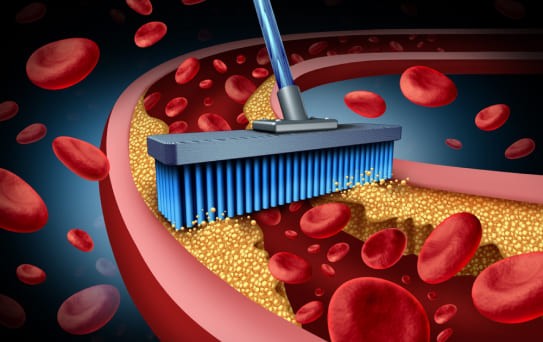
Patents Can Be Treated With Chelation Treatment In Following Disease

Natural

Non Invasive

Result Oriented

FDA Approved
Benefits To Other Diseases Also
Increment In Pumping (LVEF%)
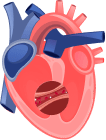
Removes Heart Blockage

Reversal Of Heart Disease
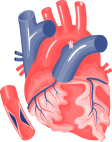
Avoid Angioplasty And Bypass
Chelation For Heart
Benefits Of Chelation Treatment
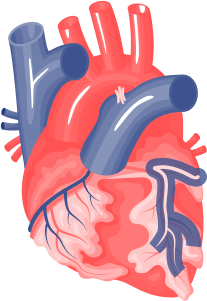
Increases Collateral Circulation
Reduce Artery Blockage
Reduces Arterial Stiffness
Remove Toxic Material From Body
FAQs
Does chelation help blood pressure?
No association between blood lead and blood pressure was found. Overall, there is no association between blood lead and blood pressure in these children with moderately high lead exposure, nor does chelation with succimer change blood pressure.
What drink cleans out arteries?
Tea is packed with phytonutrients (plant chemicals) called flavonoids, which have been shown to reduce inflammation and buildup in your arteries. Black and green tea also contain more moderate amounts of caffeine than coffee (about half the amount per cup), so it’s a great option for people who are sensitive to that.
What is chelation therapy used for?
When metals like lead, mercury, iron, and arsenic build up in your body, they can be toxic. Chelation therapy is a treatment that uses medicine to remove these metals so they don’t make you sick. Some alternative health care providers also use it to treat heart disease, autism, and Alzheimer’s disease.


