Dec 21, 2023
Heart treatment : What are the stages of heart failure?

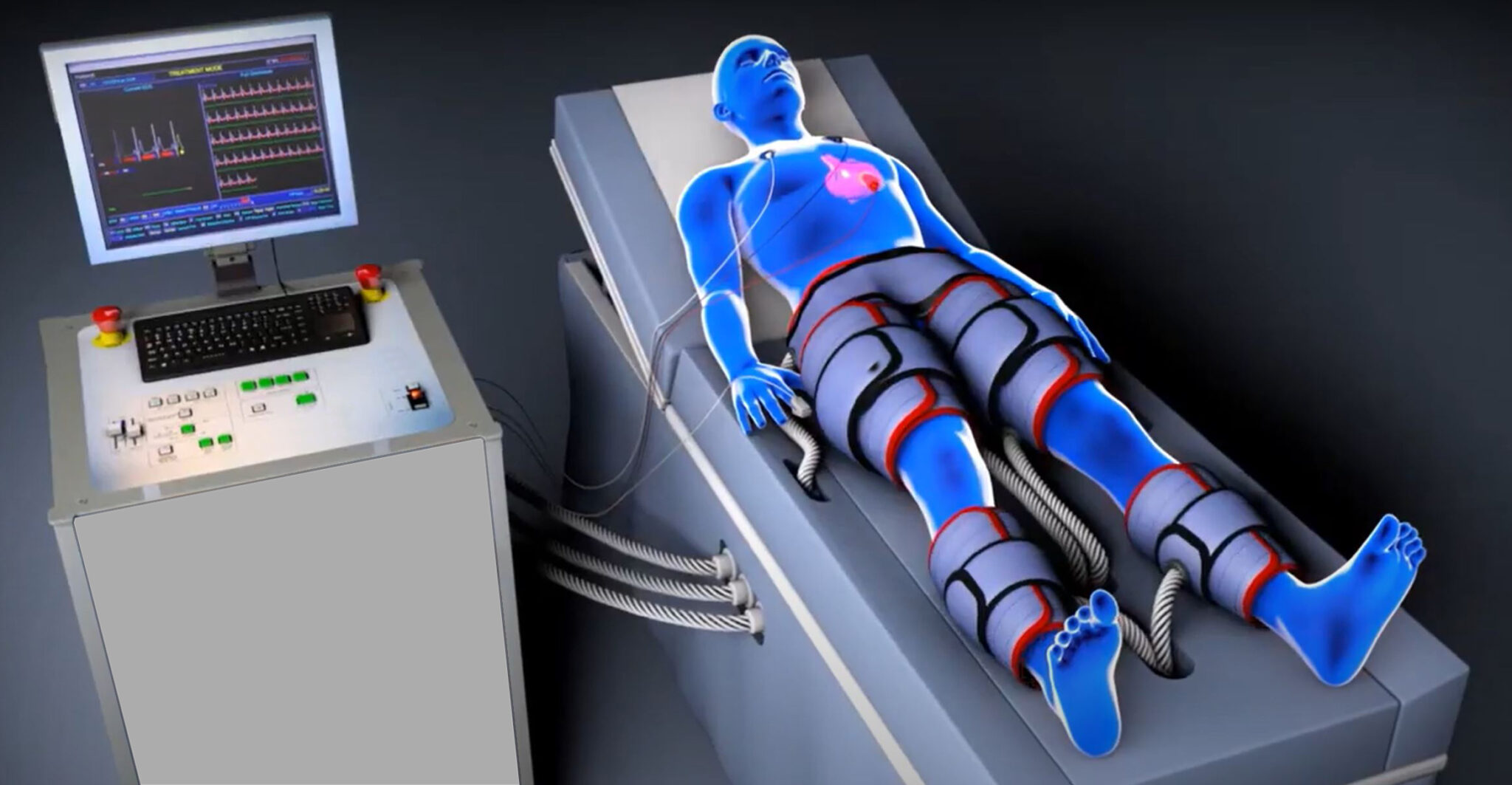
Heart treatment may include: Changing your lifestyle: This could consist of cutting saturated fats from your meals, stopping the use of tobacco products or starting a walking program. Taking medicine: You can lower blood pressure and cholesterol with medicine.
What is congestive heart failure? [Heart treatment]
Heart failure, previously known as congestive heart failure, isn't a sudden stop but a gradual decline. It's a chronic condition where the heart struggles to pump enough blood to keep the body functioning properly. This can lead to oxygen deprivation, affecting the body's ability to work at its best. [Heart treatment]Despite the name, it's important to remember that heart failure doesn't mean the heart has stopped. It's more like a weakened pump, struggling to keep up.This often happens after years of other heart conditions, such as:
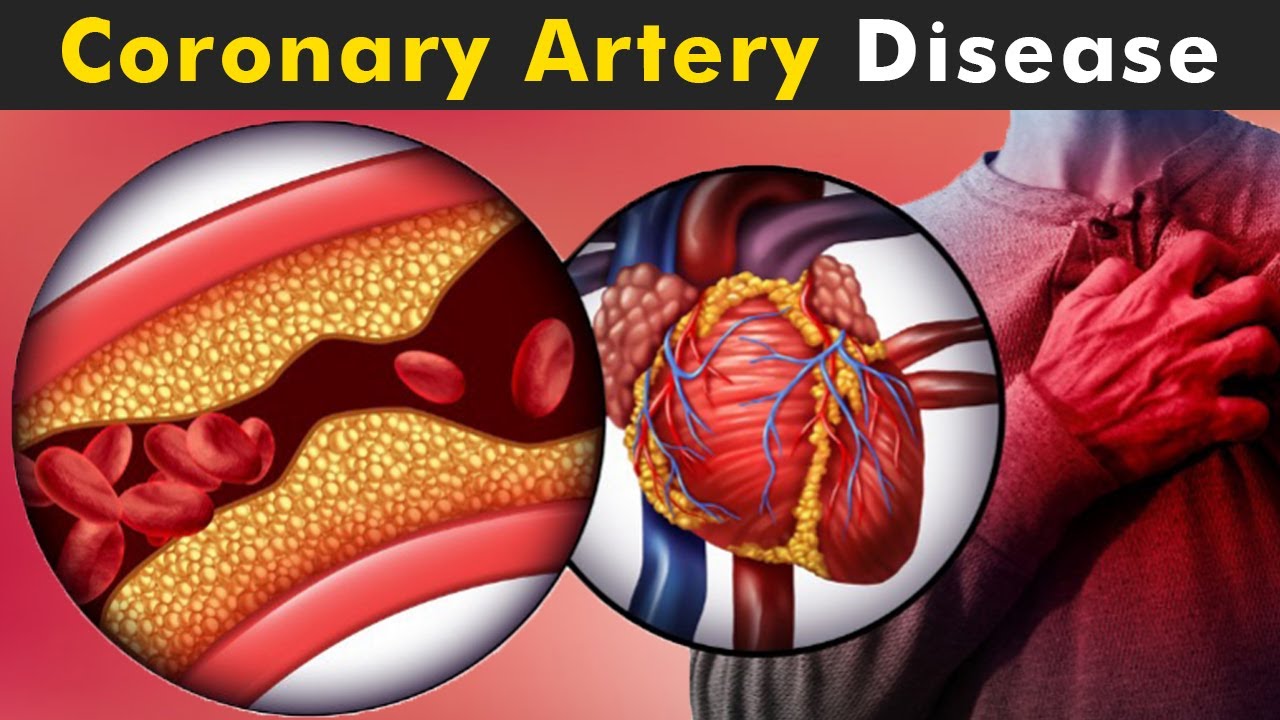
- Clogged arteries
- High blood pressure
- Valve problems
- Birth defects in the heart
- Weakening of the heart muscle
- Past heart attacks
- Irregular heartbeats
- Toxin exposure (like excessive alcohol)
What are the stages of heart failure?
Heart failure severity can be categorized into four stages, based on how well your heart pumps and the level of symptoms you experience.These symptoms commonly include:
- Difficulty breathing: This can occur during activity or while lying down.
- Swollen ankles: This is known as edema and can be a sign of fluid buildup.
- Fatigue: You may feel easily tired or exhausted even after minimal activity.
Classification based on ejection fraction
Your heart's pumping power matters for heart failure diagnosis. Ejection fraction is a key measure of its strength, showing how much blood it pumps out with each beat. [Heart treatment]Normal range:
50%-70% ejection fraction - your heart is doing great!Borderline low:
40%-50% - your heart might be recovering or slowly weakening.Struggling heart:
<40% - your heart needs help to pump enough blood.When symptoms occur with a normal ejection fraction, it's called heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). With a low ejection fraction (<40%), it's heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). And a "middle ground" (40%-49%) falls under heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).This classification helps guide treatment based on the specific weakness of your heart's pumping function.
| Ejection fraction | Symptoms of HF? | HF type |
|---|---|---|
| 50-70% (or greater) | No | No HF |
| 50-70% (or greater) | Yes | HFpEF |
| 40-50% | Yes | HFmrEF |
| <40% | Yes | HFrEF |